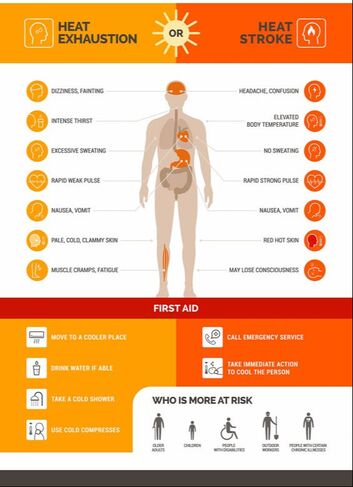
 Millions of U.S. construction workers are exposed to extreme heat in their workplace, especially when working outdoors. Of those millions, thousands of workers get sick from heat exposure each year, and some cases are fatal. The General Duty Clause (Section 5[a][1] of the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970), requires employers to provide a place of employment that is “free from recognized hazards that are causing or are likely to cause death or serious physical harm to employees.” Heat-related illness can take on five forms. 1) Heat rash is caused by clogged skin pores that hold in sweat. This prevents the body from cooling down and causing skin rash. 2) Next are heat cramps, which are painful muscle spasms caused by dehydration. 3) The third form is heat syncope, a condition causing an employee to become light-headed and sometimes faint. It is caused by dehydration resulting in decreased blood flow to the brain. 4) Even more severe is heat exhaustion, which sets in when the body loses too much water creating an electrolyte imbalance. Signs include weakness, dizziness, nausea, headache, heavy sweating, and clammy skin. 5) Finally, heatstroke is an extremely serious condition and can lead to brain damage or even death if not treated promptly and properly. Signs of a heatstroke include a rapid pulse, hot, dry skin, mental confusion, and temporary vision/hearing impairments. The first line of defense in all forms of heat related illness is to immediately get the employee out of the heat so they can cool down and hydrate. All employees should learn how to recognize a victim of heat-related illness. Evaluate the symptoms, then follow the recommended first aid actions.
Hazardous heat exposure can be prevented by employers. Supervisors should watch for warning signs of heat-related illness in their crews and should never push employees beyond their limits. Many companies offer first aid training to educate, prevent, and treat heat-related illnesses. Some preventative strategies include establishing a shaded break area, providing ice, water/sports drinks, and issuing protective clothing/cooling towels. Companies can also limit employee heat exposure through well planned work and rest schedules. Although most healthy employees will be able to acclimate to heat over a period of time, some staff may be heat intolerant. Employees can take their own preventative measures to combat heat. Drinking plenty of fluids throughout the day and staying away from alcohol and caffeine is essential. Remember to eat lighter meals while working because the more calories you consume, the more body heat you produce. Wear protective lightweight clothing and use sunblock on exposed skin. Employees should know their limits and notify a supervisor immediately if having heat illness symptoms. Occupations requiring heat exposure do not have to be dangerous. If everyone works together to take preemptive measures and watch for warning signs, heat-related illnesses can be prevented. Resources: Nation Safety Council, 2016, Heat-related Illness Occupational Safety and Health Administration, Heat American Red Cross Heat Wave Safety Comments are closed.
|


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
